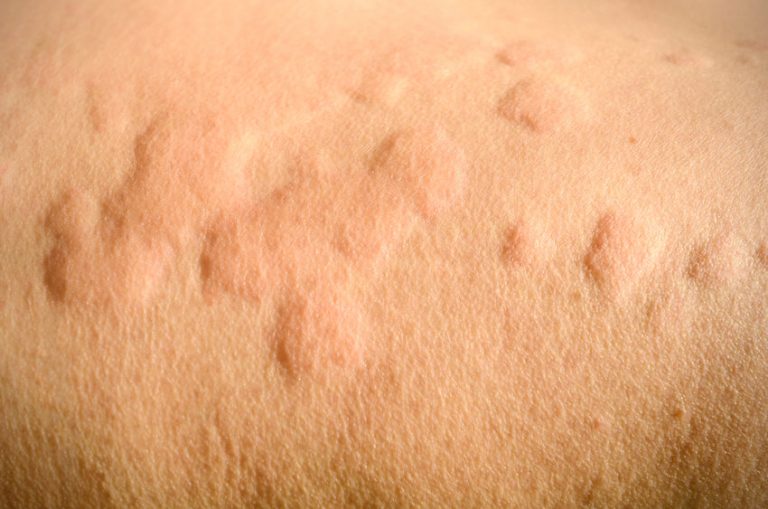
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised red bumps on the skin caused by the release of histamine and other inflammatory substances usually in response to an irritant or allergen. The most common triggers include upper respiratory tract infections, reactions to prescription drugs, and even food allergens. Sensations with these lesions include itching, stinging, prickling and pain.
Urticaria lasting less than 6 weeks is classified as acute urticaria while urticaria lasting over 6 weeks is classified as being chronic. Chronic urticaria is more common in middle-aged females while acute urticaria is more common in children. Chronic urticaria requires systemic workup by a board-certified dermatologist for identifying potential causes.
The first-line therapy to treat urticaria consists of various antihistamines. Some alternative therapies can include oral steroids, phototherapy, leukotriene inhibitors and cyclosporine. A novel injectable biologic known as Xolair (omalizumab) was approved by the FDA in March 2014 for treatment of chronic urticaria in patients over the age of 12 who did not respond to antihistamine treatment.
