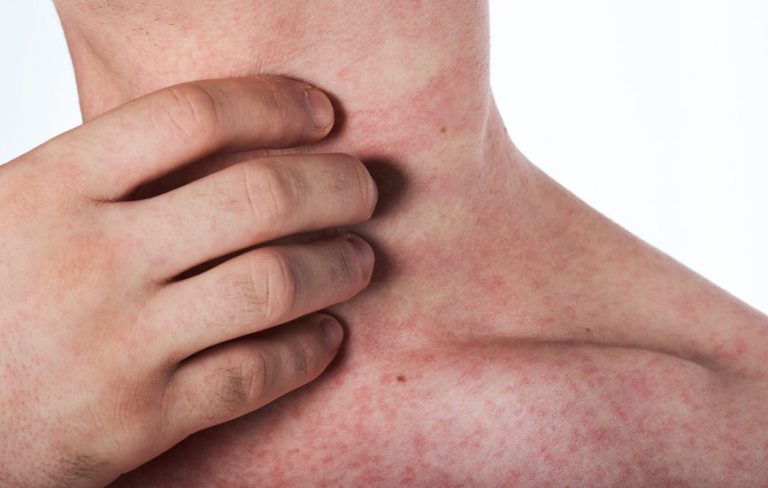
Skin allergy refers to a type of allergic contact dermatitis caused when a person’s skin comes into contact with a substance that induces an inflammatory reaction. There are two basic types of contact dermatitis: Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD) and Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD).
Irritant Contact Dermatitis (ICD) refers to a non-specific inflammatory condition that develops after skin is exposed to substances that are physically, chemically or mechanically traumatizing. Symptoms are usually confined to the area of contact, recur with additional irritant exposure and may be difficult to distinguish from allergic contact dermatitis.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that occurs from a person’s immune response to contact allergens such as fragrances, preservatives, metals, etc. ACD. can develop within hours or days and may take weeks to heal. To identify which substance(s) a person may be allergic to, Dr. Claiborne uses the T.R.U.E. Test to test 35 different allergens. This test is referred to as a ‘patch test’ which is different than the ‘prick test’ or ‘scratch test’ that requires breaking the skin to introduce the irritant. The T.R.U.E. Test is a topical test where the irritants are introduced topically. The T.R.U.E. Test only tests for skin irritants and is not used to identify allergens associated with anaphylaxis.
